Metal patching is a critical repair technique that plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of metal structures. Whether it’s repairing damage from corrosion, impact, or wear, metal patching offers a cost-effective solution that prolongs the lifespan of metal components across various industries. In this blog, we will delve into the world of metal patching, exploring what it is, when it is used, who uses it, and the steps involved in different patching methods. Additionally, we will highlight the applications of instant repair patches and introduce advanced technologies like the D523 Low-Pressure Cold Spray System.
What is Metal Patching?

Metal patching is a crucial repair technique used to restore the structural integrity and functionality of metal surfaces that have been compromised due to various forms of damage such as corrosion, wear, impact, or mechanical stress. The process involves the application of a patch or filler material to cover holes, cracks, or weakened areas, effectively extending the lifespan of the metal structure. The methods used in metal patching can range from welding and the application of epoxy to advanced techniques such as cold spray technology. The main goal of metal patching is to provide a durable and reliable repair that maintains the functionality, safety, and appearance of the component.
When is Metal Patching Used?
Metal patching is a versatile technique used across various industries, each with specific needs and applications:
Corrosion Repair
Metal structures in marine environments, industrial settings, and infrastructure are prone to corrosion due to exposure to moisture, chemicals, and harsh environmental conditions. Patching corroded areas prevents further degradation and extends the lifespan of the structure.
Impact Damage
Metal components in vehicles, machinery, and construction equipment can be damaged by collisions or falling objects. Patching provides a quick and effective way to restore these parts to their original condition without the need for extensive replacements.
Wear and Tear
Over time, metal parts can wear down due to constant use and friction. Patching worn areas helps maintain the part’s functionality and structural integrity, avoiding the cost and downtime associated with replacing entire components.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance routines often involve patching minor damages before they escalate into significant problems. This proactive approach is cost-effective and helps maintain the overall health of the equipment.
Emergency Repairs
In situations where immediate repairs are necessary to prevent operational downtime or safety hazards, metal patching offers a rapid solution that can be implemented on-site.
Who Uses Metal Patching?
Metal patching is utilised in numerous situations where metal surfaces have experienced damage but do not warrant complete replacement. Common scenarios include:
Automotive Industry
Repairing body panels, exhaust systems, frames, and other vehicle components to ensure safety, aesthetics, and prolong the lifespan of the vehicle.
Marine Industry
Fixing hulls, decks, and other structural parts of boats and ships to ensure watertight integrity and structural soundness in harsh marine environments.
Industrial Sector
Maintaining machinery, pipelines, storage tanks, and structural components in factories and plants to prevent costly downtime and ensure continuous operations.
Construction Industry
Restoring metal elements in buildings, bridges, towers, and other infrastructure to maintain safety standards and extend the lifespan of these structures.
DIY Enthusiasts
Homeowners and hobbyists use metal patching for small repairs and projects, leveraging user-friendly materials like epoxy and repair tapes for quick fixes.
Welding
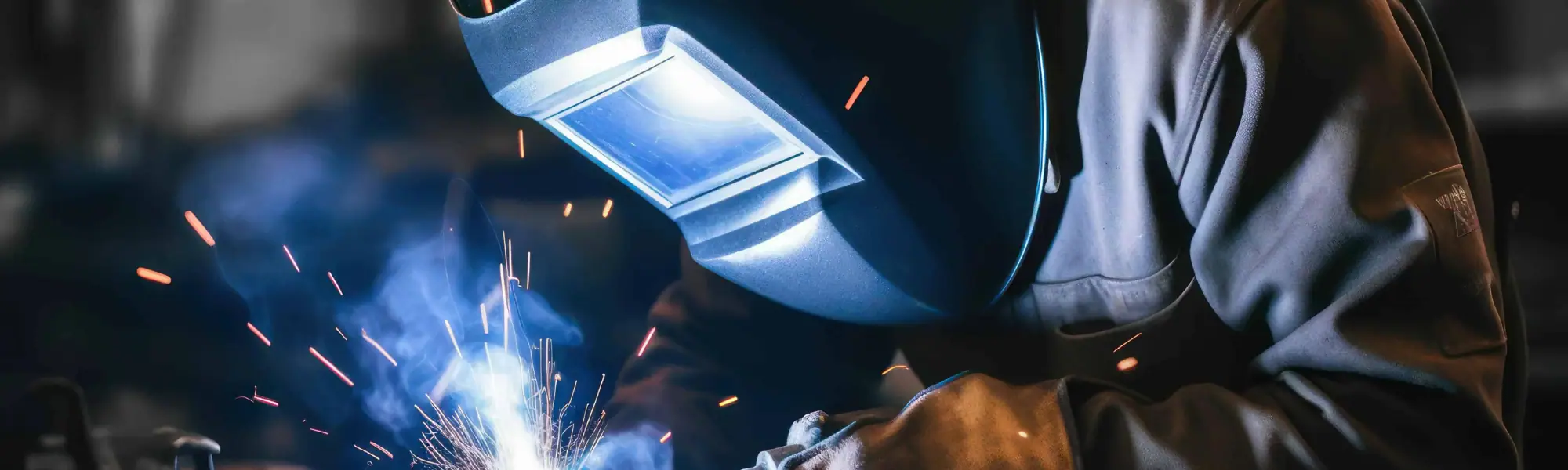

Welding is a common and highly effective method for metal patching. It involves melting a filler material to fuse it with the base metal, creating a strong, permanent bond. The steps include:
- Surface Preparation: Clean and prepare the damaged area by removing rust, paint, and debris to ensure a clean surface for the weld to bond to.
- Cutting the Patch: Cut a patch from a similar metal, ensuring it fits the damaged area precisely.
- Welding: Use appropriate welding techniques (MIG, TIG, or stick welding) to fuse the patch to the base metal. The choice of technique depends on the metal type and the specific repair requirements.
- Finishing: Grind and smooth the weld to blend it with the surrounding metal surface, ensuring a seamless repair.
Welding offers a durable and long-lasting solution, making it ideal for high-stress applications where structural integrity is crucial.
Epoxy or Tape
Epoxy and metal repair tapes are alternative patching methods suitable for quick fixes and low-stress applications. The steps include:
- Surface Preparation: Clean the damaged area thoroughly to remove any contaminants that could affect adhesion.
- Mixing Epoxy: Prepare the epoxy according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring a proper mix for maximum strength.
- Applying the Patch: Apply the epoxy or metal tape over the damaged area, ensuring full coverage. Smooth out any bubbles or wrinkles for a solid bond.
- Curing: Allow the epoxy or tape to cure and harden as per the specified time, ensuring a durable repair.
These methods are particularly useful for non-structural repairs and temporary fixes where speed and ease of application are important.
Using a UV Repair Patch to Fix Small Holes or Rust
UV repair patches are innovative solutions for small repairs, using UV light to cure the patch quickly. The steps include:
- Surface Preparation: Clean and sand the damaged area to ensure proper adhesion.
- Applying the Patch: Place the UV patch over the damage, pressing firmly to ensure good contact.
- Curing: Expose the patch to UV light, either from the sun or a UV lamp, to cure it within minutes. This method is particularly useful for quick, on-the-spot repairs.
UV repair patches offer the advantage of fast curing times, making them ideal for emergency repairs and applications where immediate use is necessary.
Applications of Instant Repair Patches
Instant repair patches are versatile and can be used in various applications, such as:
- Automotive: Quick fixes for bodywork, exhaust systems, and radiators where downtime can be costly and immediate repairs are beneficial.
- Plumbing: Sealing leaks in pipes and fittings, providing a quick and easy solution to prevent water damage.
- Roofing: Repairing metal roofs and gutters, helping to prevent leaks and further damage from weather conditions.
- HVAC Systems: Fixing ductwork and metal components in heating and cooling systems, ensuring efficient operation and preventing energy loss.
Instant repair patches are user-friendly and require minimal preparation, making them accessible for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
Cold spray is an advanced coating and additive manufacturing process that involves the deposition of fine particles onto a substrate at high velocities. Unlike traditional thermal spray processes, cold spray operates at relatively low temperatures, ensuring that the particles remain in a solid state throughout the process. This method is used to create dense, high-quality coatings and for the repair and additive manufacturing of metal components.
- Corrosion Repair: Restoring corroded surfaces without causing thermal distortion, which can weaken the metal.
- Component Restoration: Building up worn-out parts to their original dimensions, extending the life of expensive components.
- Surface Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent future damage, enhancing the durability and longevity of metal parts.
The D523 system offers a high degree of precision and control, making it suitable for applications requiring detailed and accurate repairs.
Conclusion
Metal patching is an essential technique for maintaining and repairing metal structures and components across various industries. From traditional welding to innovative UV patches and cold spray systems, there are multiple methods to suit different repair needs.
By understanding when and how to use these techniques, professionals and DIY enthusiasts can extend the life of metal parts, ensure safety, and maintain the functionality of critical systems.
Investing in the right patching method can lead to significant cost savings, reduced downtime, and improved performance of metal components. With the ongoing advancements in metal patching technologies, the future looks promising for more efficient and effective repair solutions.
Related Posts
June 3, 2024
What is Cold Spray? | Comprehensive Overview
What is cold spray? Cold spray is an advanced coating and additive…
June 2, 2024
17 CNC Machining Materials | Comprehensive Guide
Selecting the right CNC machining materials material is crucial to the success…
June 1, 2024
CNC Machining Tolerances | Comprehensive Guide
CNC machining tolerances are essential for achieving the desired precision and…