In the realm of manufacturing, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software plays a pivotal role in shaping the way products are designed, developed, and brought to life. Let’s delve into the world of CAD software and explore its significance in the manufacturing industry.
What is CAD software?
CAD software, short for Computer-Aided Design, is a digital tool used by engineers, designers, and architects to create precise and detailed 2D and 3D models of products, components, and structures. It allows users to visualise, simulate, and analyse designs before they are physically constructed, facilitating the design process and enabling iterative improvements.
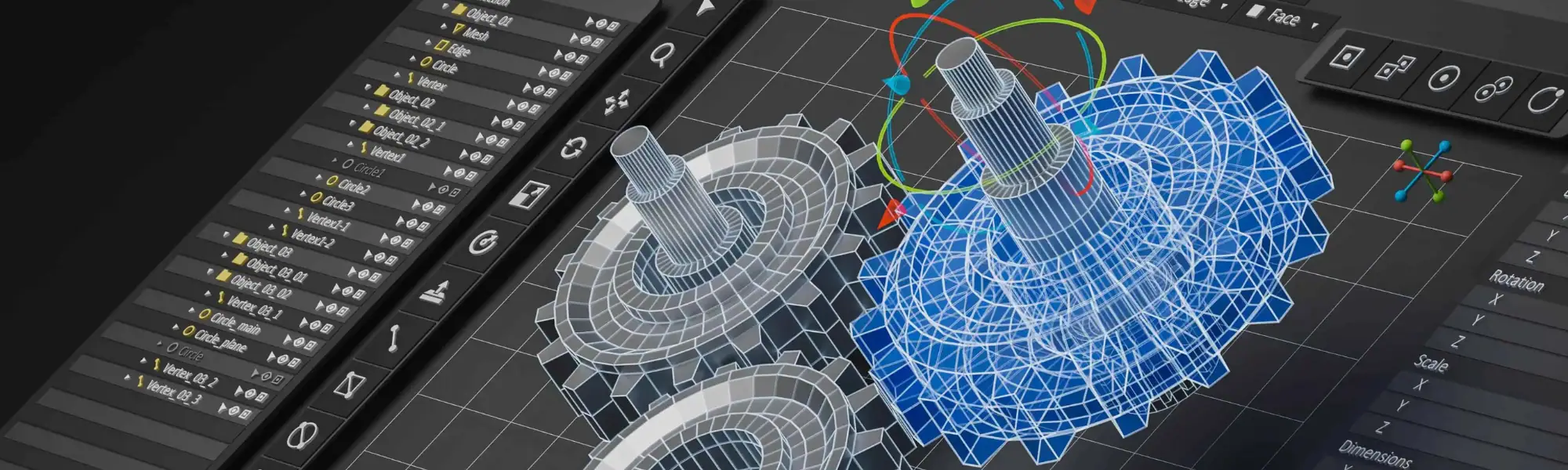

How does computer-aided design work?
CAD software operates on sophisticated algorithms that translate user inputs into graphical representations of objects. Users can manipulate these digital models using a variety of tools and commands to modify dimensions, shapes, and properties. Additionally, CAD software often integrates with other design and analysis tools, allowing for seamless collaboration and workflow optimisation.
How to choose CAD software
Selecting the right CAD software for your manufacturing needs requires careful consideration of factors such as functionality, compatibility, ease of use, and cost. It’s essential to assess your specific requirements and evaluate different software options based on their features, support, and reputation within the industry.
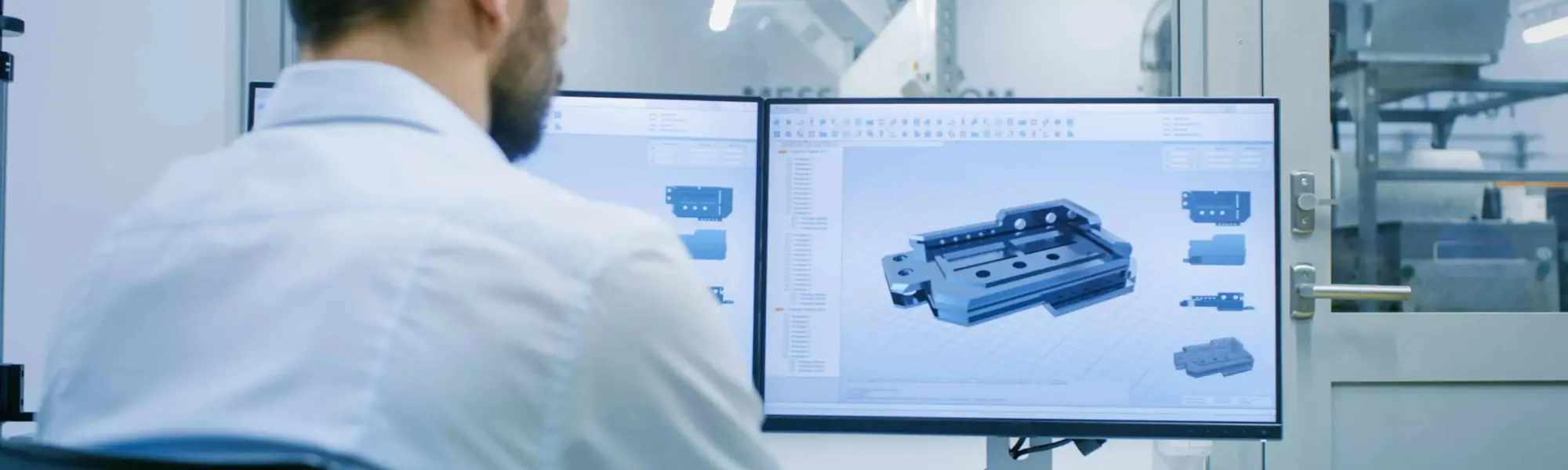

Types of CAD Software
CAD software comes in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and industries. Some common types of CAD include parametric modelling, direct modelling, surface modelling, and solid modelling. Each type offers unique advantages and capabilities, catering to different design requirements and preferences.
Advantages of CAD software
The adoption of CAD software offers numerous benefits to manufacturers, including increased productivity, improved design accuracy, reduced time-to-market, and enhanced collaboration. By streamlining the design process and providing powerful visualisation tools, CAD software empowers manufacturers to innovate and iterate more efficiently.
CAD software features
Modern CAD software boasts an array of features designed to streamline the design process and enhance productivity. These features may include parametric modelling, assembly modelling, simulation and analysis tools, rendering capabilities, and compatibility with industry standards such as STEP and IGES.
Who uses CAD?
CAD software is utilised by a wide range of professionals across various industries, including mechanical engineers, product designers, architects, civil engineers, and electrical engineers. It serves as a fundamental tool for conceptualising, designing, and refining products, structures, and systems.

How do different industry professionals use CAD software?
In the manufacturing industry, CAD software is indispensable for creating detailed product designs, generating engineering drawings, simulating product performance, and generating CNC machining instructions. It enables engineers and designers to iterate on designs, validate concepts, and optimise product functionality and manufacturability in industries such as CNC engineering.
The Evolution and Future of CAD Software
Historical Development
The evolution of CAD software dates back to the 1960s when the first rudimentary systems were developed to assist with complex calculations and drafting tasks. Over the decades, CAD software has undergone significant advancements, evolving from simple 2D mechanical drafting tools to sophisticated 3D modeling systems. Key milestones in the development of CAD software include:
- 1960s: The inception of CAD with systems like SKETCHPAD, which introduced basic graphical manipulation of objects.
- 1970s: The introduction of commercial CAD software such as AutoCAD, which brought CAD capabilities to a wider audience.
- 1980s: The development of parametric modelling, allowing for more complex and flexible design modifications.
- 1990s: The integration of CAD with other design and manufacturing tools, leading to the development of integrated CAD/CAM systems.
- 2000s: The rise of 3D modelling and simulation capabilities, enhancing the ability to visualise and test designs digitally.
- 2010s: The incorporation of cloud computing, enabling collaborative design and real-time data sharing.
Future Trends in CAD Software
The future of CAD software is shaped by emerging technologies and evolving industry needs. Key trends that are likely to influence the development of CAD software include:
- Cloud-Based CAD: The shift towards cloud-based CAD solutions will enable greater collaboration, flexibility, and accessibility, allowing users to work from anywhere and on any device.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI-driven tools will enhance design automation, optimise processes, and provide intelligent insights to improve design quality and efficiency.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality: The integration of AR and VR technologies will offer immersive design experiences, allowing users to interact with and visualise models in a more intuitive and realistic manner.
- Generative Design: Advanced algorithms will enable generative design, where software generates multiple design alternatives based on specified constraints and objectives, helping engineers explore innovative solutions.
- Sustainability: CAD software will increasingly incorporate tools and features to support sustainable design practices, helping engineers and designers create environmentally friendly products and structures.
Conclusion
CAD software revolutionises the manufacturing process by providing powerful tools for design, visualisation, and analysis. As a leading provider of manufacturing solutions, Bredo offers comprehensive CAD services to support your design and engineering needs. Contact us today to learn more about how our CAD capabilities related to CNC machining that can drive innovation and efficiency in your manufacturing projects.
Related Posts
June 3, 2024
What is Cold Spray? | Comprehensive Overview
What is cold spray? Cold spray is an advanced coating and additive…
June 2, 2024
17 CNC Machining Materials | Comprehensive Guide
Selecting the right CNC machining materials material is crucial to the success…
June 1, 2024
CNC Machining Tolerances | Comprehensive Guide
CNC machining tolerances are essential for achieving the desired precision and…