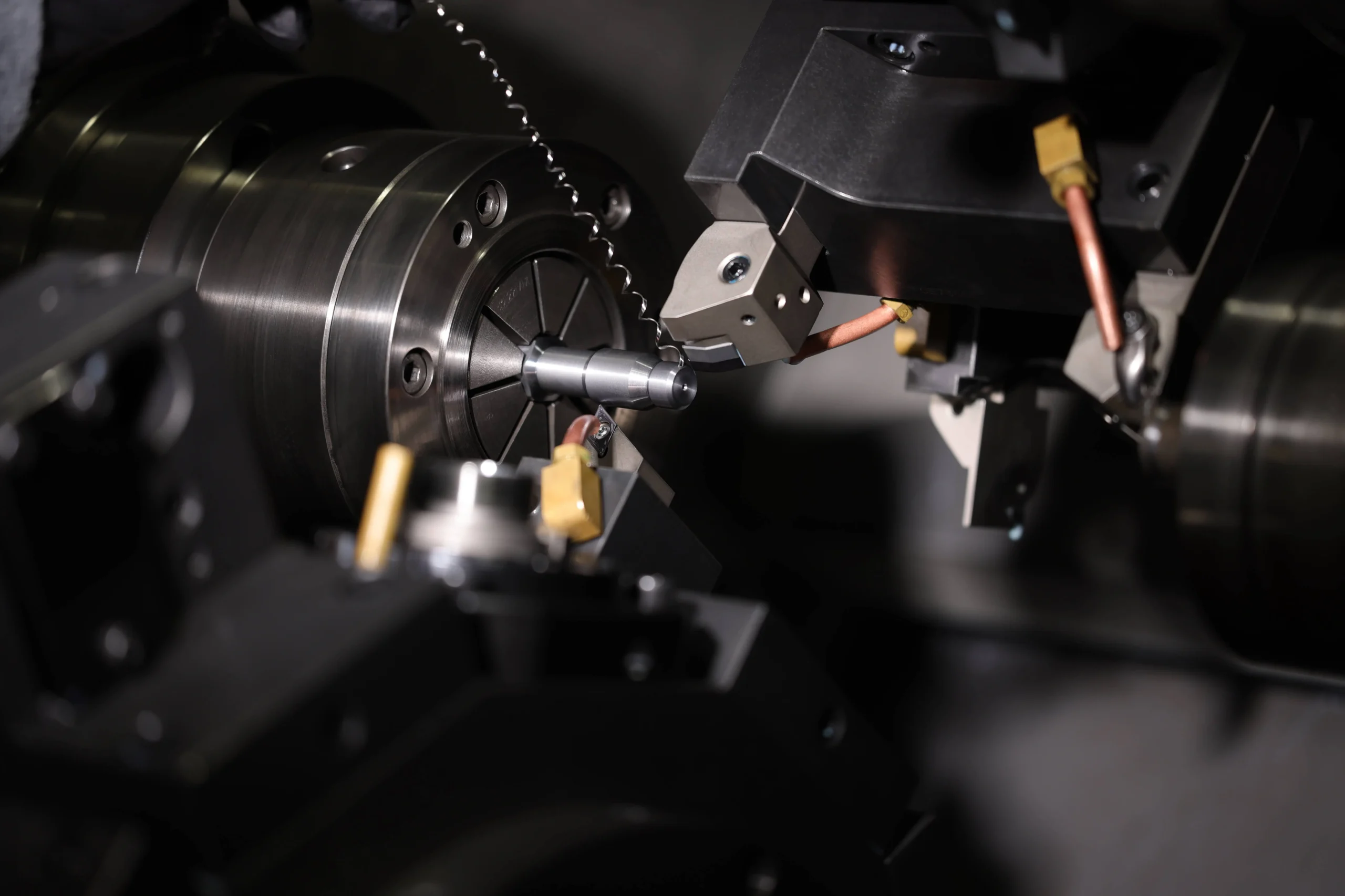
In the realm of modern manufacturing, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) plays a pivotal role in shaping precision engineering processes. But what exactly is CNC, and how does it revolutionise the manufacturing landscape? Let’s delve into the fundamentals of this innovative technology.
What is Computer Numerical Control?
Computer Numerical Control, commonly referred to as CNC, is a sophisticated manufacturing technology that automates the operation of machine tools via computer programming. It replaces traditional manual control methods with precise, automated commands, allowing for the creation of complex and intricate components with unparalleled accuracy.

How Does CNC Machining Work?
In CNC machining, a computerised control system interprets design specifications from Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software and translates them into precise movements and commands for cutting tools and machinery. This level of automation enables manufacturers to produce intricate parts and components with consistent quality and high repeatability.
Benefits of CNC Technology
Computer numerical control technology offers a multitude of benefits to manufacturers, enhancing various aspects of the production process and providing significant advantages over traditional manual methods. Here are some key benefits of CNC technology:
Enhanced Precision
Computer numerical control machines can achieve incredibly tight tolerances, resulting in parts with exceptional accuracy and consistency. The precision of CNC machining ensures that each component meets exact specifications, reducing the likelihood of errors and the need for manual adjustments. This high level of accuracy is particularly crucial in industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive, where precision is paramount.
Increased Efficiency
Automation reduces human error and minimises production downtime, resulting in faster turnaround times and increased productivity. CNC machines can operate continuously, 24/7, without the need for constant human supervision. This capability significantly boosts production capacity and allows manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and high-demand situations effectively.
Versatility
Computer numerical control machines can fabricate a wide range of materials, from metals and plastics to composites and wood, making them suitable for diverse manufacturing applications. Whether it’s prototyping, custom manufacturing, or mass production, computer numerical control technology can adapt to various requirements and materials, offering flexibility and scalability in production processes.
Cost-Effectiveness
While initial setup costs may be higher, CNC machining offers long-term cost savings through reduced scrap, labour, and material waste. The automation of the manufacturing process minimises the need for manual labour, lowering labour costs and increasing overall efficiency. Additionally, the precision of CNC machining reduces material waste, optimising resource utilisation and contributing to cost savings over time.
Improved Safety
Computer numerical control machines enhance workplace safety by reducing the need for manual intervention in potentially hazardous tasks. Operators can program and monitor the machines from a safe distance, minimising the risk of accidents and injuries. The automation of repetitive and dangerous tasks further ensures a safer working environment for employees.
Consistent Quality
Computer numerical control technology ensures consistent quality in every production run, maintaining uniformity and adherence to specifications across all manufactured parts. This consistency is crucial for industries where high-quality standards are essential, such as medical devices, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing. Consistent quality reduces the need for rework and enhances customer satisfaction.
Applications of CNC Machining

Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, CNC machining is used to manufacture critical components that require high precision and reliability. Examples include:
- Engine Parts: Turbine blades, fuel nozzles, and engine casings.
- Structural Components: Wing spars, fuselage frames, and landing gear parts.
- Avionics: Housings for electronic systems and navigation equipment.
The stringent quality and safety standards in aerospace demand the exceptional accuracy and consistency that computer numerical control machining provides.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on CNC machining for the production of various components, including:
- Engine Components: Cylinder heads, engine blocks, and crankshafts.
- Transmission Parts: Gearboxes, transmission cases, and gears.
- Interior and Exterior Parts: Dashboard panels, trim pieces, and custom body parts.
CNC machining enables the mass production of automotive parts with precise tolerances and high repeatability, ensuring the performance and reliability of vehicles.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, CNC machining is essential for creating intricate and miniaturised components used in various devices, such as:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphone frames, laptop cases, and heat sinks.
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Drilling holes and milling PCB prototypes.
- Connectors and Housings: Precision connectors, enclosures, and brackets.
The ability to machine small, detailed parts with high accuracy makes CNC technology invaluable for electronics manufacturing.
Medical Industry
The medical industry utilises CNC machining to produce medical devices and components that require precision and sterility, including:
- Surgical Instruments: Scalpels, forceps, and orthopedic tools.
- Implants and Prosthetics: Hip joints, dental implants, and custom prosthetics.
- Diagnostic Equipment: Housings and components for MRI machines, CT scanners, and laboratory instruments.
CNC machining ensures that medical components meet stringent regulatory standards and deliver reliable performance in critical applications.
Energy Industry
CNC machining plays a crucial role in the energy sector by manufacturing components for power generation and distribution, such as:
- Turbine Components: Blades, rotors, and casings for wind, steam, and gas turbines.
- Oil and Gas Equipment: Drill bits, valve bodies, and pump components.
- Renewable Energy: Parts for solar panels, wind turbines, and hydroelectric generators.
The durability and precision of computer numerical control machined parts help enhance the efficiency and reliability of energy systems.
Industrial Manufacturing
In general industrial manufacturing, CNC machining is used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Tool and Die Making: Molds, dies, and jigs for manufacturing processes.
- Custom Machinery: Components for automated machinery and production lines.
- Prototyping: Rapid prototyping of new products and components for testing and development.
CNC technology enables manufacturers to produce high-quality tools and equipment that drive innovation and efficiency in various industrial processes.
Consumer Goods
CNC machining is also employed in the production of high-quality consumer goods, such as:
- Sporting Goods: Bicycle components, golf club heads, and fishing reel parts.
- Home Appliances: Parts for kitchen appliances, power tools, and HVAC systems.
- Luxury Items: Custom jewellery, watch components, and designer accessories.
The ability to create finely detailed and aesthetically pleasing parts makes CNC machining ideal for manufacturing premium consumer products.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology has revolutionised the manufacturing industry, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. By harnessing the power of CNC machining, manufacturers can unlock new possibilities and drive innovation in product development. Partner with Bredo for all your CNC engineering needs and experience the difference precision engineering can make.
At Bredo, we leverage state-of-the-art CNC technology to deliver precision-engineered components tailored to your specifications. Contact us
Related Posts
June 3, 2024
What is Cold Spray? | Comprehensive Overview
What is cold spray? Cold spray is an advanced coating and additive…
June 2, 2024
17 CNC Machining Materials | Comprehensive Guide
Selecting the right CNC machining materials material is crucial to the success…
June 1, 2024
CNC Machining Tolerances | Comprehensive Guide
CNC machining tolerances are essential for achieving the desired precision and…