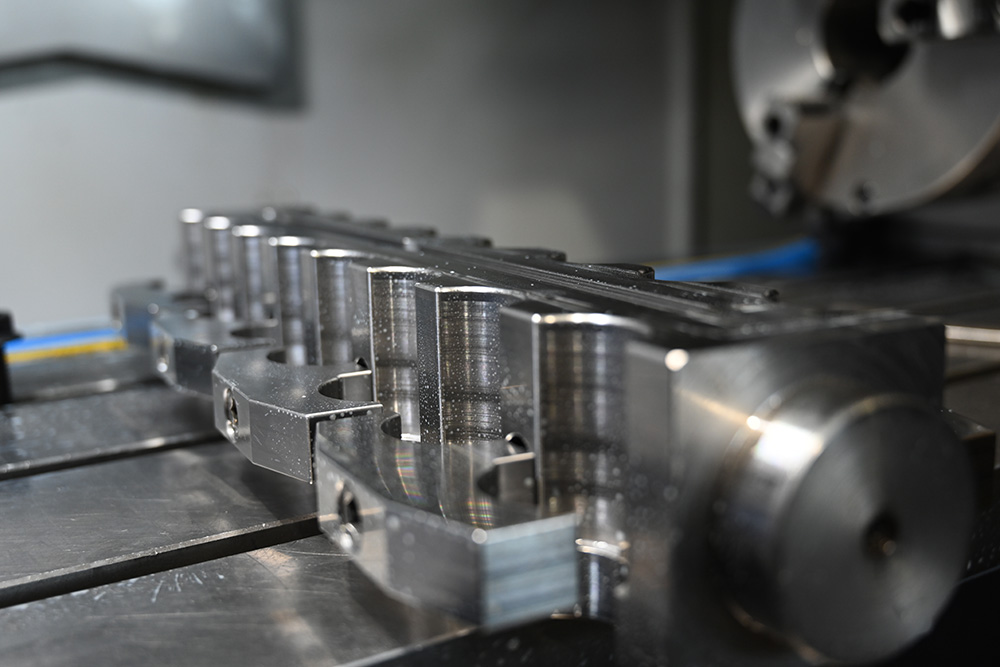
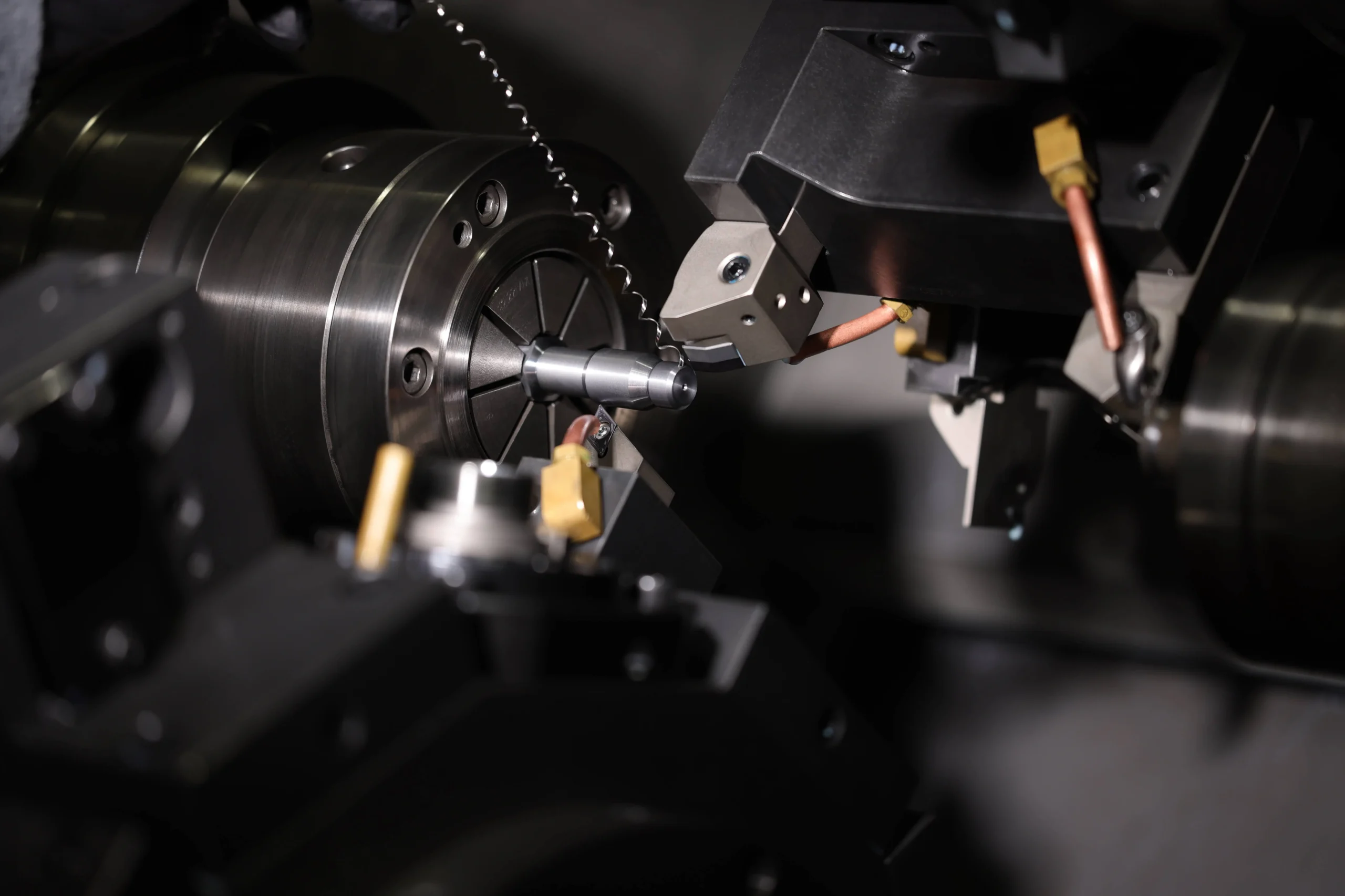
There are many advantages of CNC machining, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining represents a significant advancement over traditional machining methods. By automating the control of machining tools through computers, CNC machining has brought about numerous benefits that enhance precision, efficiency, and overall productivity in manufacturing.
What are the Advantages of CNC Machining?
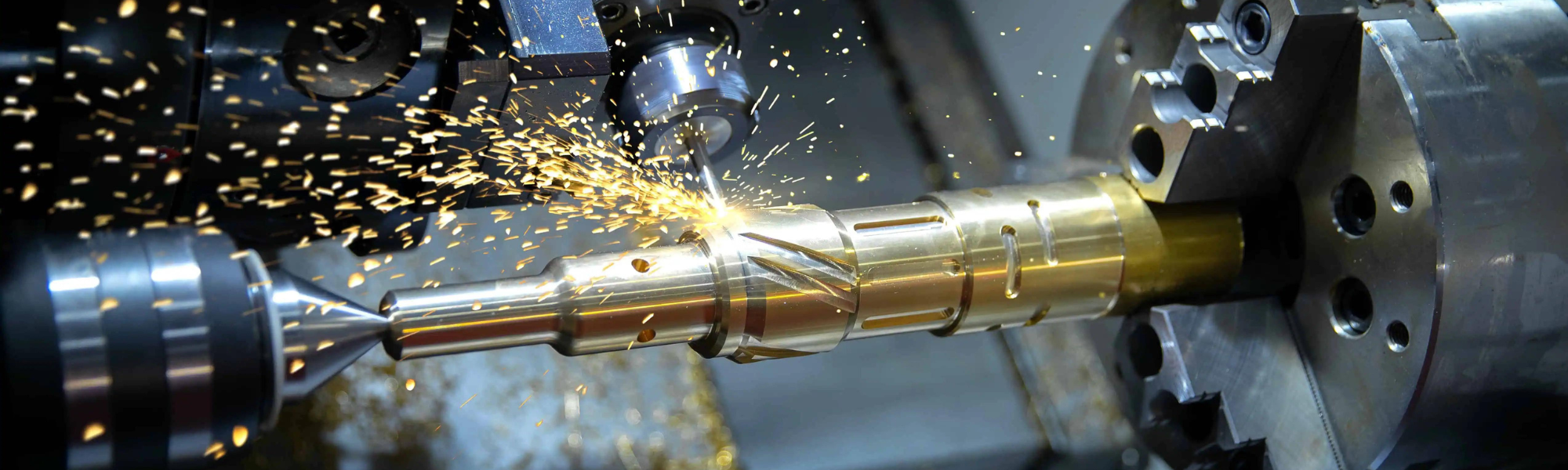

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining stands out as a revolutionary technology in the manufacturing industry. Unlike traditional machining methods that require manual intervention and are prone to human error, CNC machining leverages computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) to automate the production process. This shift has resulted in numerous benefits, significantly enhancing accuracy, speed, efficiency, and safety. Below, we delve into these benefits in greater detail.
Accuracy in CNC Machining
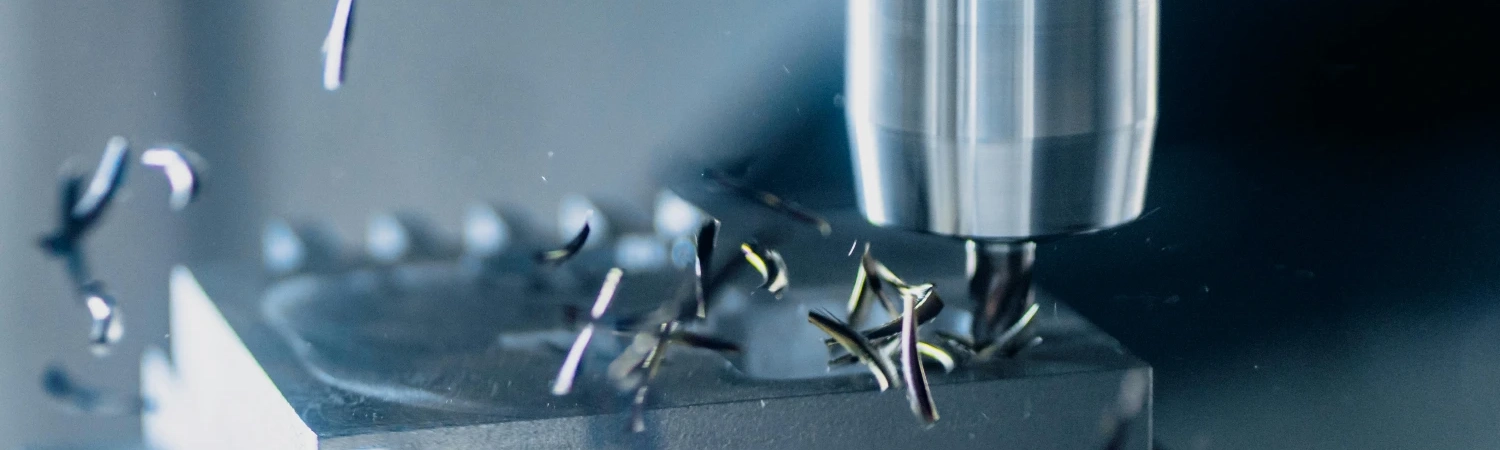

One of the most notable advantages of CNC machining is its unparalleled accuracy. This precision is achieved through the integration of advanced computer technology and automated control systems, which allow CNC machines to produce parts with extremely tight tolerances, often within a few microns. This level of precision is difficult, if not impossible, to achieve with manual machining methods, which rely heavily on the skill and experience of the operator.
Precision and Tolerances
CNC machines operate based on precise instructions from CAD (Computer-Aided Design) files. These files provide detailed specifications and measurements, ensuring each part is produced to exact dimensions. This precision is maintained consistently across production runs, resulting in high-quality, uniform parts. CNC machines are capable of achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches (±0.0254 mm), making them ideal for applications requiring exacting standards.
For instance, in the aerospace industry, components such as turbine blades and engine parts must meet stringent specifications to ensure the safety and performance of aircraft. Even a slight deviation in the dimensions of these parts can lead to catastrophic failures. CNC machining ensures that each component is manufactured to the exact specifications, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing overall safety.
Production Speed and Increased Efficiency in CNC Machining
CNC machining stands out for its remarkable ability to boost production speed and efficiency, revolutionising manufacturing processes across industries. By leveraging advanced automation and precise programming, CNC machines deliver unparalleled performance in terms of turnaround times, production volumes, and operational efficiency.
Continuous Operation
One of the key factors contributing to the speed and efficiency of CNC machining is its ability to operate continuously, 24/7, once the initial setup is complete. Unlike traditional machining methods that rely on manual operation and periodic supervision, CNC machines can run unattended, executing programmed instructions with precision and consistency. This continuous operation minimises idle time and maximises throughput, allowing manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and handle large production volumes efficiently. For example, in automotive manufacturing, where demand for parts is often high and production schedules are tight, CNC machining enables seamless round-the-clock operation, ensuring a steady supply of components to assembly lines.
Rapid Turnaround Times
The rapid turnaround times offered by CNC machining are a game-changer for industries that require quick production cycles and on-demand manufacturing. Once a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) file is uploaded to the CNC machine, the production process begins immediately, without the need for manual intervention or setup. This streamlined workflow drastically reduces lead times, enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly to customer orders and market demands.
In sectors such as consumer electronics and aerospace, where product life cycles are short and innovation cycles are rapid, CNC machining provides the agility and flexibility needed to stay competitive. Manufacturers can iterate designs, produce prototypes, and ramp up production rapidly, bringing new products to market faster and capturing market opportunities more effectively.
Advantages for Operators of CNC Machines
Operators of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines enjoy several significant advantages over traditional machining methods. From reduced physical strain to enhanced job satisfaction, CNC technology transforms the working environment for machine operators, promoting safety, efficiency, and productivity.
Reduced Physical Strain
One of the primary benefits for operators of CNC machines is the reduction in physical strain associated with manual machining. Traditional machining methods often require operators to perform repetitive, physically demanding tasks, such as operating handwheels, adjusting tooling, and lifting heavy workpieces. This constant exertion can lead to fatigue, musculoskeletal injuries, and long-term health issues.
In contrast, CNC machines are controlled by computer programs, eliminating the need for manual intervention in the machining process. Operators can program the machine, load materials, and monitor the operation from a safe distance, minimising direct contact with moving parts and hazardous machinery. This reduction in physical strain not only improves operator comfort but also reduces the risk of workplace injuries, leading to a safer and healthier working environment.
Focus on Monitoring and Quality Control
With CNC machining, operators can shift their focus from manual operation to monitoring the machine’s performance and ensuring the quality of the output. Rather than spending hours performing repetitive tasks, operators can dedicate their time to overseeing the machining process, verifying dimensions, and inspecting finished parts for accuracy and quality.
This transition from manual labour to supervisory roles allows operators to leverage their skills and expertise more effectively, contributing to higher-quality products and greater overall efficiency. By closely monitoring the machining process, operators can detect any issues or anomalies early on and take corrective action to prevent costly errors or defects.
CNC Machining Cost
While the initial investment in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machinery may seem daunting, the long-term cost benefits and return on investment are substantial. CNC machining offers a range of advantages that contribute to cost savings across various aspects of manufacturing operations, from labour and material expenses to production efficiency and quality control.
Reduced Labour Costs
One of the most significant cost-saving advantages of CNC machining is the reduction in labour expenses. Traditional machining methods often require skilled operators to perform manual tasks such as setup, tooling changes, and monitoring of machining operations. These labour-intensive processes not only incur significant payroll costs but also pose risks of human error and variability in production outcomes.
With CNC machining, much of the manual labour is replaced by automated processes controlled by computer programs. Once the CNC machine is programmed and set up, it can operate autonomously, minimising the need for direct human intervention. Operators oversee the machining process, ensuring quality control and troubleshooting as needed, but their role is primarily supervisory rather than hands-on. As a result, manufacturers can reduce labour costs, improve operational efficiency, and reallocate human resources to more value-added tasks.
Minimise Material Waste
CNC machining also contributes to cost savings by minimising material waste during the manufacturing process. Traditional machining methods often involve extensive manual cutting, shaping, and milling of raw materials, leading to significant material loss through offcuts, scrap, and rework. This wastage not only drives up material expenses but also increases production time and energy consumption.
In contrast, CNC machines are programmed to optimise material usage and minimise waste through precision cutting and efficient nesting of parts. Advanced software tools allow manufacturers to maximise the utilisation of raw materials, reducing scrap and offcuts to a minimum. Additionally, CNC machines can perform complex machining operations with high accuracy, reducing the need for secondary finishing processes and further minimising material waste.
Accurate Repetition
One of the standout features of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is its ability to achieve accurate repetition, delivering consistent and uniform parts with unmatched precision. This capability is instrumental in industries that demand high volumes of identical components, where consistency and quality are paramount. Unlike traditional machining methods, which rely on manual operation and are susceptible to human error, CNC machining ensures reliable replication of designs across all produced parts, contributing to enhanced product quality and adherence to industry standards.
Precision and Consistency
CNC machining excels in producing identical parts repeatedly with consistent accuracy, thanks to its advanced automation and computer-controlled processes. Once a design is programmed into the CNC machine, it can replicate the same geometries and dimensions precisely, without the variability inherent in manual machining. This level of precision is critical for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where even minor deviations can have significant consequences for performance and safety.
By eliminating human error and ensuring uniformity across all manufactured parts, CNC machining delivers unparalleled consistency in product quality, meeting the stringent requirements of industry standards and regulatory certifications. Manufacturers can rely on CNC technology to produce components with tight tolerances and intricate geometries consistently, regardless of batch size or production volume.
Less Labour Required
CNC machining revolutionises manufacturing by significantly reducing the need for manual labour. Unlike traditional machining methods that rely heavily on human intervention, CNC machines operate autonomously once programmed, requiring minimal human oversight. This transformative automation allows manufacturers to optimise their workforce allocation, reallocating human resources to tasks that demand specialised expertise, such as quality control and process optimisation.
By automating repetitive tasks and routine operations, CNC machining streamlines production processes, enhances productivity, and minimises the risk of human error. Operators can focus on monitoring the machining process, ensuring the quality of output, and fine-tuning parameters to optimise efficiency. This shift towards a more supervisory role not only increases productivity but also fosters a safer working environment by reducing manual labour and associated risks of injury.
Furthermore, the reduced dependency on manual labour translates to lower labour costs for manufacturers. With CNC machines handling the bulk of machining tasks, companies can achieve higher output with fewer personnel, leading to significant cost savings in the long run. This cost-effectiveness enables manufacturers to remain competitive in today’s dynamic market while delivering high-quality products efficiently and economically.
Effective Prototyping
CNC machining stands as a cornerstone of effective prototyping, offering unparalleled capabilities to designers and engineers in testing and refining their concepts swiftly and precisely. This rapid prototyping prowess revolutionises the product development cycle, enabling companies to bring innovative ideas to market faster than ever before.
The speed and precision of CNC machines allow for the rapid production of intricate parts with exceptional accuracy. Designers can quickly translate their digital models into physical prototypes, facilitating hands-on evaluation and validation of form, fit, and function. This iterative process empowers teams to identify and address design flaws early in the development phase, minimising costly revisions and delays down the line.
Moreover, CNC machining facilitates the production of small batches of parts cost-effectively. This flexibility enables manufacturers to conduct comprehensive testing and validation on prototypes, ensuring that they meet performance criteria and regulatory requirements before scaling up for full-scale production. By producing small quantities of parts on-demand, companies can iterate designs quickly and respond promptly to feedback and market demands.
Safety of Operators
Ensuring the safety of operators is paramount in any manufacturing environment, and CNC machining provides substantial safety advantages compared to traditional methods. Central to these advantages is the design of CNC machines themselves, which are enclosed systems that protect operators from exposure to moving parts and potential hazards, significantly reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Unlike manual machining processes that require direct interaction with cutting tools and machinery, CNC machining operates autonomously once programmed, minimising the need for operators to be in close proximity to the equipment during operation. This automation reduces the risk of accidents associated with human error, fatigue, and distractions, fostering a safer working environment for personnel.
Furthermore, the automated nature of CNC machining enables operators to monitor the manufacturing process from a safe distance, mitigating the need for direct physical involvement in production tasks. Operators can oversee the machining process, observe machine performance, and address any issues that arise without exposing themselves to potential hazards.
Conclusion
Operators of CNC machines enjoy numerous advantages that enhance their safety, efficiency, and job satisfaction. By reducing physical strain, enabling focused monitoring and quality control, fostering a positive work environment, and providing opportunities for skill development, CNC technology transforms the role of machine operators in modern manufacturing. As CNC machining continues to evolve and become more prevalent, operators will play a crucial role in driving innovation, productivity, and competitiveness in the industry.
Related Posts
June 3, 2024
What is Cold Spray? | Comprehensive Overview
What is cold spray? Cold spray is an advanced coating and additive…
June 2, 2024
17 CNC Machining Materials | Comprehensive Guide
Selecting the right CNC machining materials material is crucial to the success…
June 1, 2024
CNC Machining Tolerances | Comprehensive Guide
CNC machining tolerances are essential for achieving the desired precision and…